Legal company structures for Global Expansion for
Indian SMEs & Start-Up and EB5 Source of funds
Legal structures empower Indian companies, including SMEs and startups, to expand globally by ensuring regulatory compliance, tax efficiency, and risk mitigation under FEMA rules. These frameworks, from subsidiaries to holding companies, are vital tools for seamless international operations, as demonstrated by giants like Tata and Infosys.
For EB-5 investors, they also streamline source-of-funds documentation, proving lawful origins to USCIS. Our Law firm recently assisted Indian EB5 investors by making a legal structure.
Core Legal Structures for Global Expansion
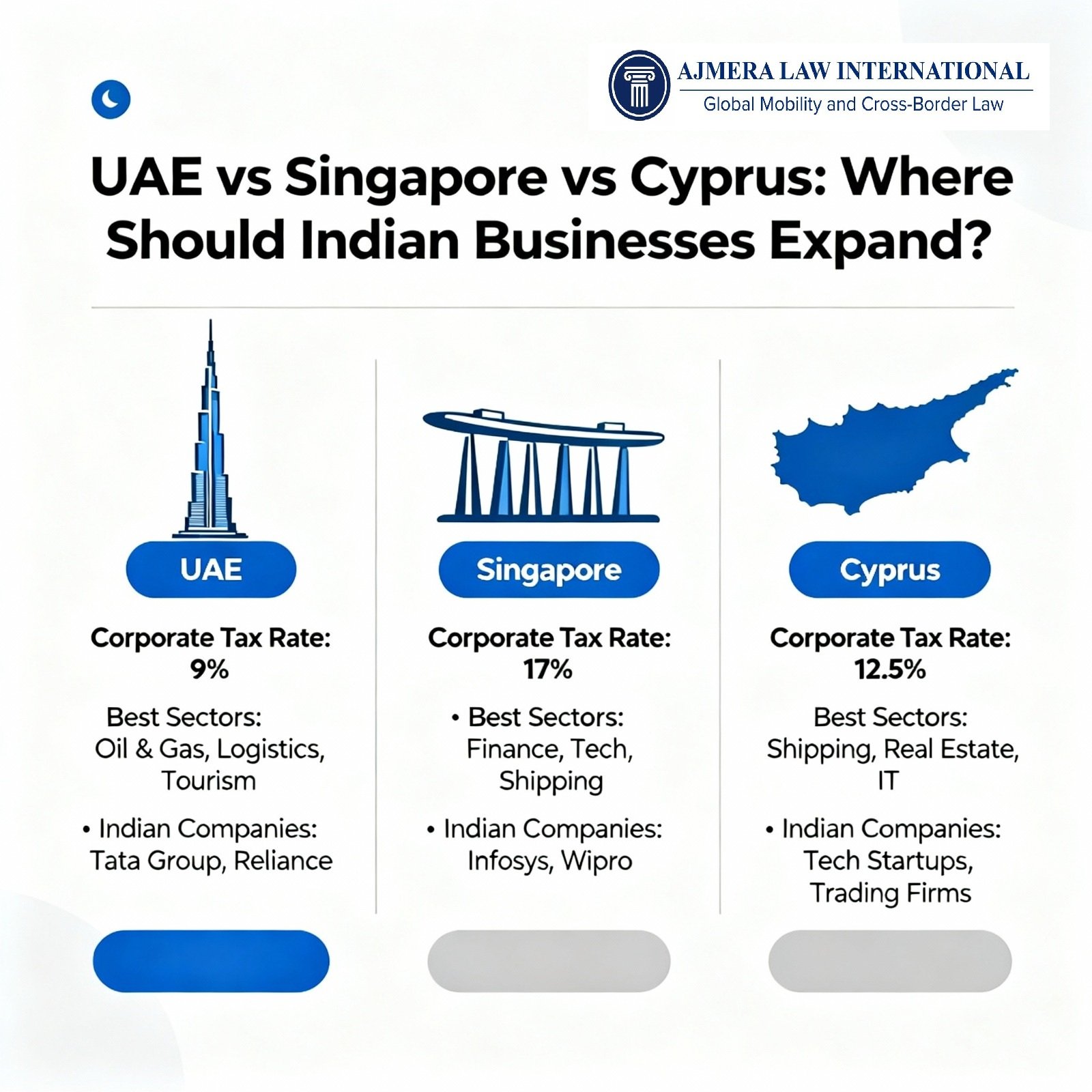
Indian entities adopt wholly-owned subsidiaries for limited liability and local compliance, branches for operational simplicity, joint ventures for market partnerships, and holding entities in hubs like Singapore for IP centralization and royalties.
Under FEMA Overseas Investment Rules 2022, investments route via automatic approval up to 400% of net worth or LRS (USD 250,000 per individual), avoiding multi-layer limits and prohibited sectors like real estate. POEM rules require foreign boards to meet abroad with independent directors to prevent Indian tax residency.
Strategies for SMEs and Startups
Indian SMEs and DPIIT-recognized startups simplify global entry with subsidiaries in the US, UAE, or Singapore, leveraging Udyam registration for export incentives and Startup India for FDI ease.
Initial steps include liaison offices or branches (RBI-notified), progressing to JVs for local expertise, all under bona fide business criteria—no passive investments.
Flipkart’s Singapore holding enabled Walmart integration;
Byju’s US entities fueled edtech growth, optimizing fundraising and compliance.
EB-5 Investors: Structuring Source of Funds
EB-5 applicants use proprietorships, partnerships, or private limited companies to trace funds from profits, gifts, or sales, backed by 5-year tax returns, audited P&Ls, bank statements, and CA certifications.
On the other hand global company structures may provide clean records for USCIS path-of-funds analysis, though dividends incur DDT; partnerships suit family liquidity proofs via LRS or without LRS remittances. FEMA compliance ensures seamless fund transfers abroad, avoiding scrutiny. This may avoid TCS in many cases.